An 8-bit priority encoder can be designed using two 4-bit priority encoders and a multiplexer.
- The input is divided into two groups of 4 bits each:
- Lower 4 bits → handled by PENC4 (P0)
- Upper 4 bits → handled by PENC4 (P1)
- A multiplexer then selects the output of the higher-priority group.
How It Works
- If any bit in the upper nibble (Din[7:4]) is
1, it has higher priority than the lower nibble. Dout[2]indicates whether the upper nibble is active.- The lower 2 bits of
Doutcome from the selected 4-bit encoder.
Block Diagram
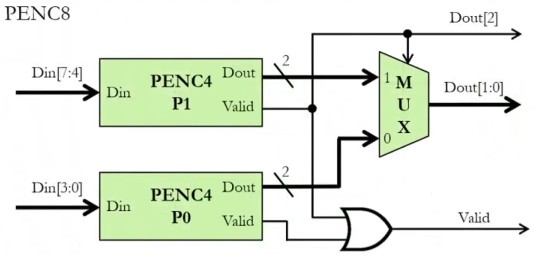
Dout[2]= 1 when upper block (PENC4 for Din[7:4]) is active.
Verilog Implementation
module PENC8(Din, Dout, Valid);
input [7:0] Din;
output [2:0] Dout;
output Valid;
wire [1:0] Dout_0, Dout_1;
wire Valid_0, Valid_1;
// Instantiate two 4-bit priority encoders
PENC4 P0(.Din(Din[3:0]), .Dout(Dout_0), .Valid(Valid_0));
PENC4 P1(.Din(Din[7:4]), .Dout(Dout_1), .Valid(Valid_1));
// Determine final output
assign Dout[2] = Valid_1; // MSB indicates upper block
assign Dout[1:0] = (Valid_1) ? Dout_1 : Dout_0; // Select correct block
assign Valid = Valid_0 | Valid_1; // OR of both valid signals
endmodule