Program Blocks in Testbenches
- Testbenches should be written in
programblocks, notmodules. - Execution starts with
initialblocks at time 0. alwaysblocks are not allowed inprogram.- Use
initial + foreverloop instead to mimicalways.
- Use
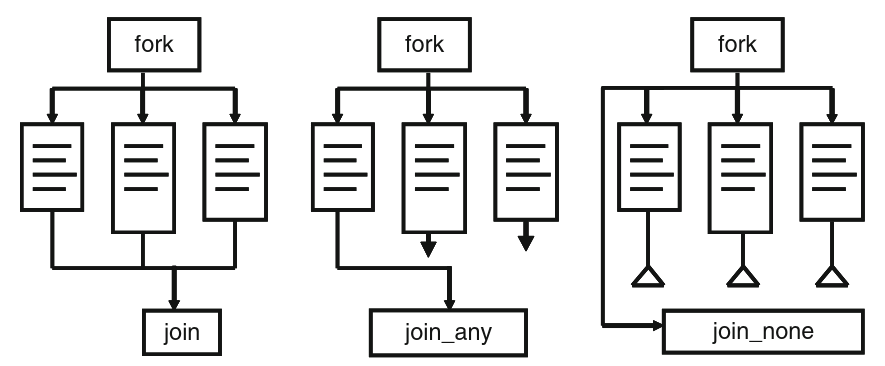
Grouping Statements
- Classic Verilog:
begin … end→ statements run sequentially.fork … join→ statements run in parallel, but all must finish before continuing.- Limitation: inflexible for long-running processes → rarely used in testbenches.
SystemVerilog Threading Enhancements
- New fork-join constructs:
fork … join_none→ parent continues immediately, child threads run in background.fork … join_any→ parent continues when any one child finishes.
Thread Synchronization & Control
Threads coordinate using IPC (interprocess communication) constructs:
- Events & Event Control (
@event) - Wait statements (
wait (cond)) - Disable statements (stop a process/thread)
- Semaphores (manage access to shared resources)
- Mailboxes (pass messages/data between threads)
fork...join
program top;
initial begin
$display("@%0t: start fork...join example", $time);
#10;
$display("@%0t: sequential after #10", $time);
fork
$display("@%0t: parallel start", $time);
#50;
$display("@%0t: parallel after #50", $time);
#10;
$display("@%0t: parallel after #10", $time);
begin
#30;
$display("@%0t: sequential after #30", $time);
#10;
$display("@%0t: sequential after #10", $time);
end
join_none
$display("@%0t: after join", $time);
#80;
$display("@%0t finish after #80", $time);
end
endprogram
join wait for everything to be done before it proceeds. join any continue after any one of them done. non would wait for them. Not that they all starts at the same time.
Setting independent variables in different Threads
initial begin
for (int j=0; j<3; j++)
fork automatic int k = j; // Make copy of index
$write(k); // Print copy
join_none
#0 $display;
end
Disabling a Thread
parameter TIME_OUT = 1000;
task wait_for_tr(Transaction tr);
fork
begin
// Wait for response, or some maximum delay
fork : timeout_block
wait (bus.cb.addr != tr.addr);
#TIME_OUT $display("@%0d: Error: timeout", $time);
join_any
disable timeout_block;
$display("@%0d: Addr match %d", $time, tr.addr);
end
join_none
endtask
This version introduces two threads inside a fork...join_any, where:
- The
waitstatement monitors for the expected condition (bus.cb.addr != tr.addr). - A parallel thread triggers after a delay (
TIME_OUT) to print an error message if the wait takes too long.
If the correct bus address returns quickly enough:
- The
waitcompletes. join_anyexecutes.disableterminates the remaining thread.
If the bus address does not match in time:
- The time-out message is displayed.
join_anyexecutes.disablekills the waiting thread.
Disabling Multiple Threads
SystemVerilog extends this concept with the disable fork statement, allowing you to stop all child threads spawned from the current thread.
⚠️ Warning:
Usingdisable forkcan unintentionally stop too many threads, including those created by routine calls.
To avoid this, always surround target code with afork...joinblock to limit the scope of thedisable forkstatement.
Limiting the Scope of a disable fork
initial begin
wait_for_tr(tr0); // Spawn thread 0
// Create a thread to limit scope of disable fork
begin
wait_for_tr(tr1); // Spawn thread 1
fork
wait_for_tr(tr2); // Spawn thread 2
join
// Stop threads 1 & 2, but leave 0 alone
#(TIME_OUT/2) disable fork;
end
join
end
Explanation
This code structure demonstrates how to control which threads are stopped by limiting the scope of disable fork.
Thread hierarchy:
| Thread ID | Description | Parent Scope |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | wait_for_tr(tr0) |
Outside all forks |
| 1 | wait_for_tr(tr1) |
Inside fork block |
| 2 | wait_for_tr(tr2) |
Spawned within thread 1 |
| 3–4 | (inner fork calls) | Child threads under 1 |
Behavior:
wait_for_tr(tr0)starts thread 0 — it’s outside the fork block.- Inside the
fork...join, new threads (1,2,3,4) are spawned. - After a delay (
#(TIME_OUT/2)),
thedisable forkstatement stops only threads under thread 1’s scope. - Thread 0 remains unaffected since it’s outside the fork scope.
Using a Label to Stop Specific Threads
initial begin
wait_for_tr(tr0); // Spawn thread 0
begin : threads_1_2
wait_for_tr(tr1); // Spawn thread 1
wait_for_tr(tr2); // Spawn thread 2
end
// Stop threads 1 & 2, but leave 0 alone
#(TIME_OUT/2) disable threads_1_2;
join
end