Protocol-Layer Packets
- Communication between a host controller root port and a SuperSpeed device uses Protocol-Layer packets.
- All packets (with one exception) are 16 bytes in size and are referred to as Header packets.
- The DATA Header packet may include a Data Packet Payload (DPP):
- Payload size: 1–1024 bytes
USB 2.0 Token/Data/Handshake Shortcomings
USB 2.0 protocols suffer from four main limitations:
- Inefficient three-packet sequence (Token → Data → Handshake)
- Shared broadcast bus, increasing power consumption
- Polled flow control, relying heavily on NAK packets
- Limited error handling, with only three retries before software intervention
SuperSpeed protocols address these issues as outlined below.
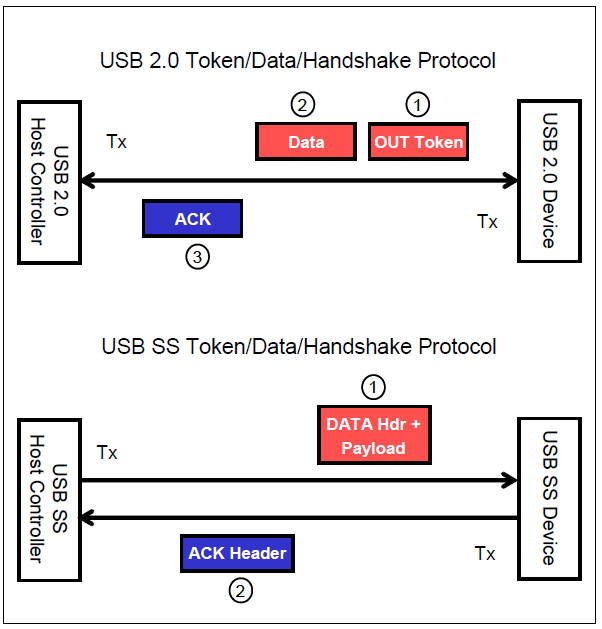
1. Inefficient Token/Data/Handshake Sequence
USB 2.0
- A typical transaction requires three packets:
- Token → DATA → ACK
- (Isochronous transfers omit the handshake packet.)
SuperSpeed (SS)
- Uses a two-packet transaction:
- DATA Header packet (includes token information)
- Data Packet Payload (DPP)
- This reduces protocol overhead and improves efficiency.
Key Benefit:
Lower latency and reduced packet overhead per transaction.
2. Broadcast Bus and Power Consumption
USB 2.0
- Uses a shared broadcast bus:
- Packets are sent to all devices of the same speed.
- Each device must decode the address to determine relevance.
- Both data and handshake packets may be broadcast, increasing unnecessary link activity and power usage.
SuperSpeed
- Uses unicast transactions:
- Packets are sent only to the target device.
- Only links along the path from the root port to the device are activated.
- Routing information is embedded in packets and used by SS hubs to forward traffic to the correct downstream port.
Key Benefit:
Significant reduction in power consumption and unnecessary link activity.
3. Polled Flow Control
USB 2.0
- Relies on repeated polling:
- Endpoints are frequently polled to check readiness.
- Often results in repeated NAK responses, wasting bus bandwidth.
- Affects most endpoint types (except Isochronous).
SuperSpeed
- Uses a poll-once protocol:
- Host accesses an endpoint once.
- If not ready, the device responds with NRDY (Not Ready).
- The host waits until the device sends ERDY (Endpoint Ready) before retrying.
- In some cases, devices can send ERDY without being polled again.
Key Benefit:
Eliminates excessive retries and dramatically improves bus efficiency.
4. Error Handling and Reporting
USB 2.0
- Performs packet error checks.
- Allows up to three retries per transaction.
- If all retries fail, the error is reported to software.
SuperSpeed
- Retains the same error-checking mechanism and three-retry limit.
- Applies these checks end-to-end at the protocol layer.
Key Benefit:
Maintains robustness while integrating with improved SS protocol efficiency.
Data Bursting
- SuperSpeed normally requires each DATA payload to be acknowledged by an ACK Header packet.
- Data Bursting allows:
- Multiple DATA payloads to be transmitted before receiving the first ACK.
- Burst limits are defined by the Max Burst value in the Endpoint Companion Descriptor.
Specifications:
- Maximum burst size: 16
- Maximum payload per DATA packet: 1024 bytes
- Maximum burst transfer size: 16 KB
Key Benefit:
Reduced latency and improved throughput.
Bulk Streaming
- Bulk Streaming is an optional feature available only for bulk endpoints.
- Designed to manage multiple data streams efficiently.
Standard Bulk Endpoints
- One endpoint buffer maps to one main memory buffer.
Bulk Streaming
- Expands buffer support to nearly 64k buffers.
- Uses a 16-bit Stream ID (in header packets) to:
- Select a specific endpoint buffer
- Map it to a corresponding main memory buffer on the host
Key Benefit:
Supports high-throughput, parallel data streams with reduced software overhead.