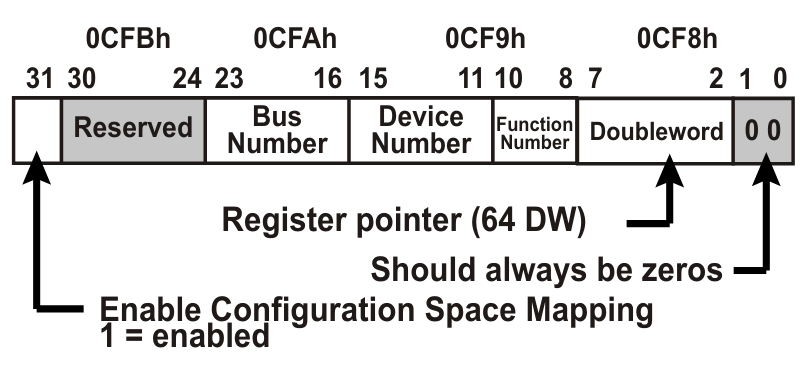
Since I/O address space is limited, PCI uses an indirect method to access configuration registers. This process happens in two steps:
Step 1: Write to the Address Port
- CPU writes to the Configuration Address Port at IO address CF8h.
- This tells the North Bridge which PCI function should be accessed.
- The address encodes:
- Bus number (0–255) → Which PCI bus
- Device number (0–31) → Which device on that bus
- Function number (0–7) → Which function in the device
- Register number (0–63 dwords = 256 bytes) → Which configuration register
Step 2: Access the Data Port
- CPU then performs an IO read or write to the Configuration Data Port at CFCh.
- The North Bridge uses the address set in Step 1 and:
- Generates a Configuration Read (if CPU read)
- Generates a Configuration Write (if CPU write)
- This transaction goes to the PCI bus and reaches the specified device/function/register.
Address Structure